This blog is only available in English
Share datsets across workspaces
Power BI offers the possibility to share datasets across Workspaces. The advantage is that data governance, security and the ideal of self-service BI can be maintained. We will answer the following three questions regarding this topic.
- Why is sharing datasets across workspaces useful?
- When can we share datasets across workspaces?
- How is self-service BI, security and governance guaranteed?
The advantage of sharing datasets
For many years, cubes have been a popular choice for sharing data and giving users the possibility to do their own analysis. Even though cubes are great products, maintaining and extending cubes is usually the task for the IT department or external consultants. Datasets in the Power BI Service are in fact tabular cubes. They are created during data modelling in Power BI Desktop.
The flexibility and user-friendliness of the Power BI desktop makes creating and maintaining the model easier than traditional cubes. It is exactly because of this user-friendliness that many others,besides the IT department, are now able to create datasets. This makes data governance a challenging job. Every upside has its downside, right?
What might happen is that the IT department limits the creation of datasets. Removing the possibility for business users to create and extend the analysis they want to do: limiting self-service BI. The following question arises: how can we maintain data governance and security with a self-service BI tool such as Power BI?
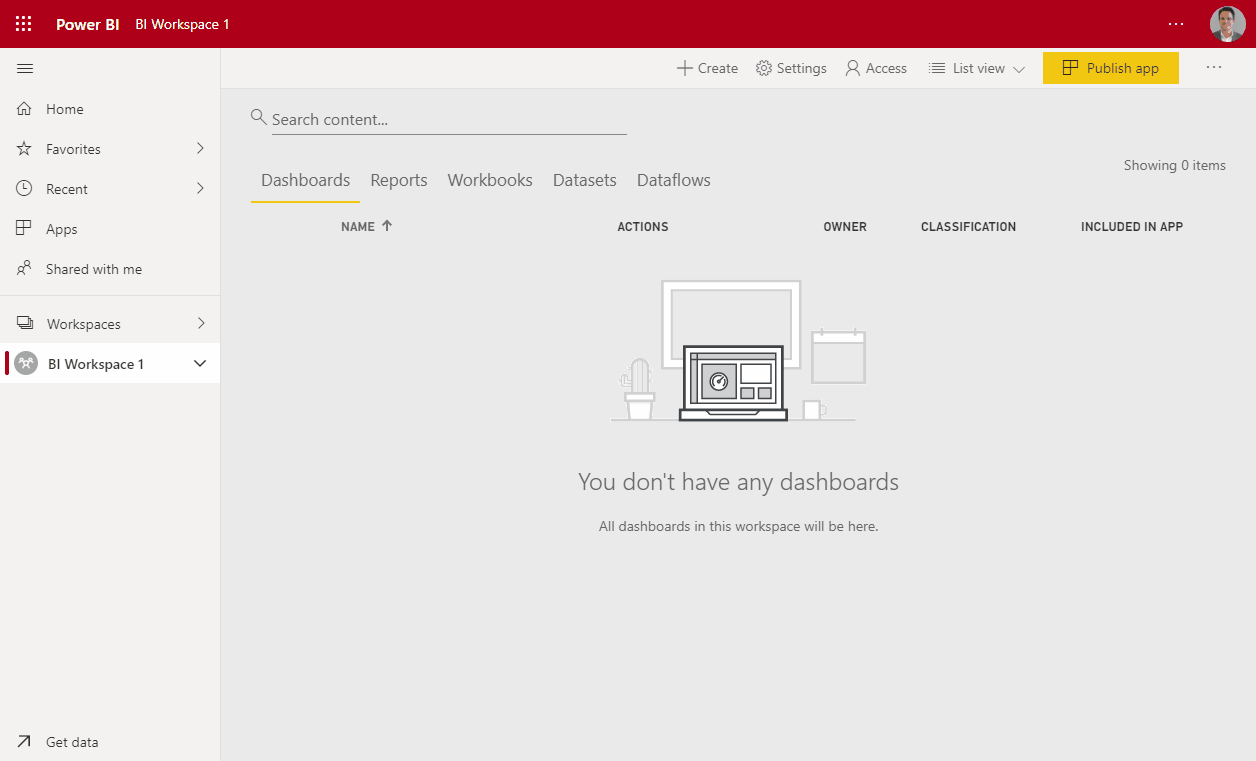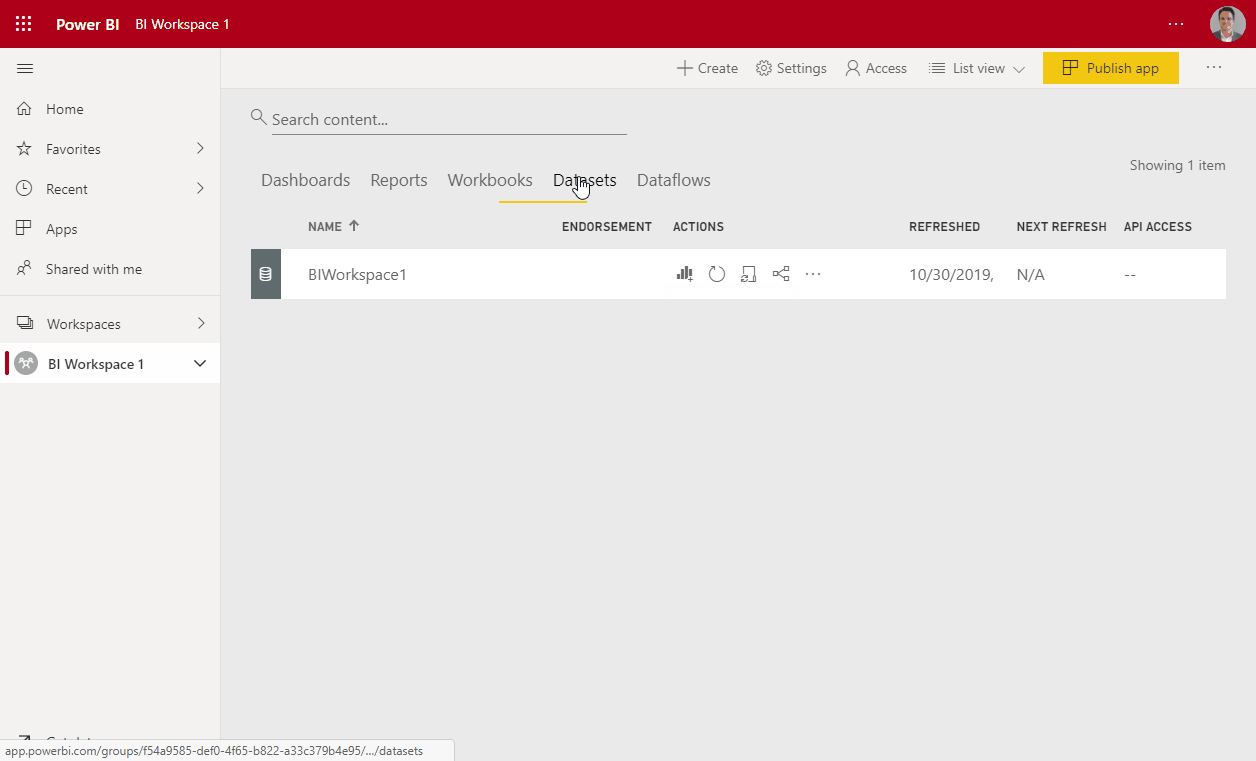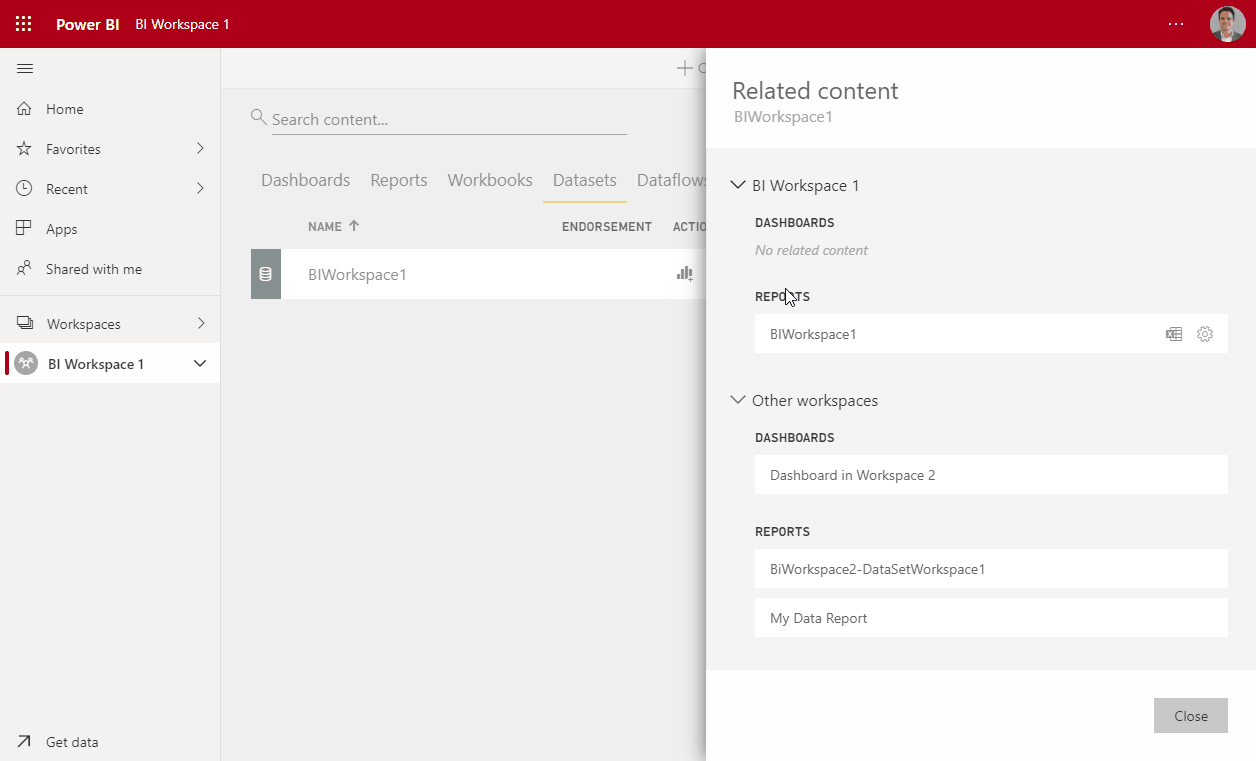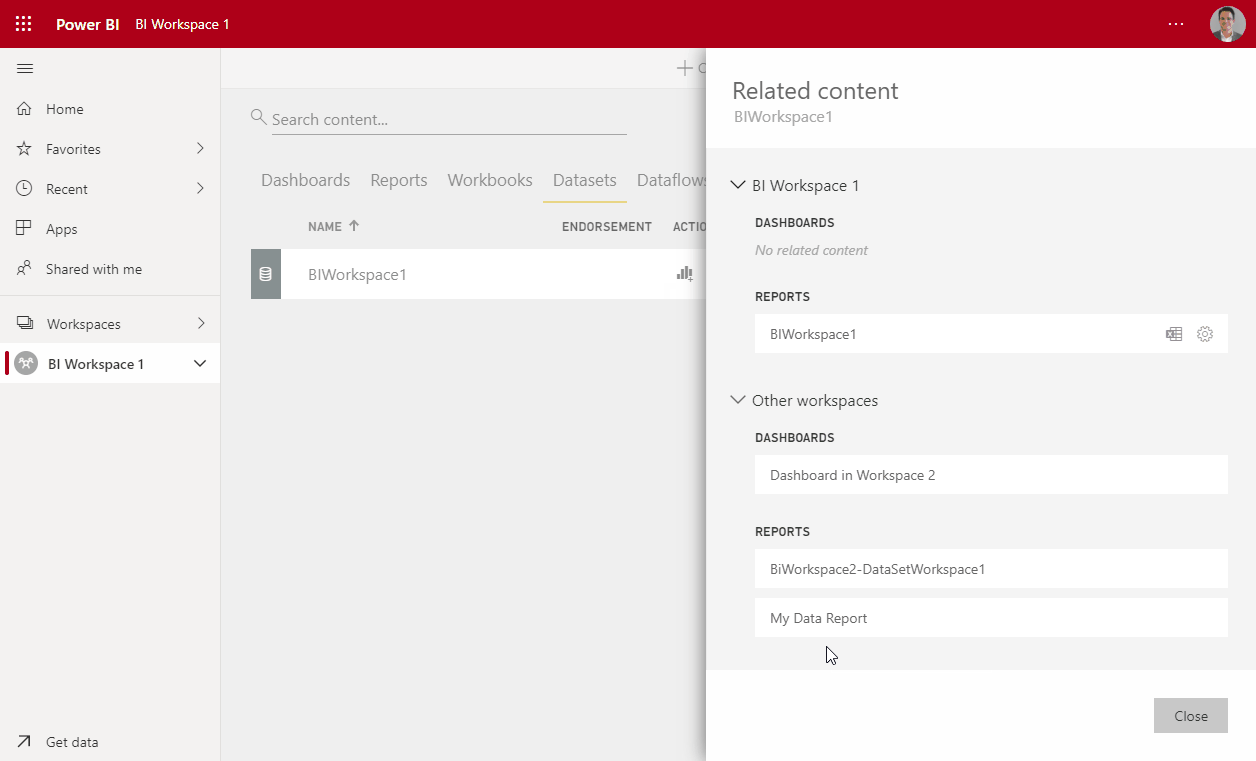
One of the answers is sharing datasets among workspaces. In order to ensure data governance, you can share a dataset without the ability to edit the dataset. Users can still create their own reports and create measures. The Power Query Editor, however, is off limits. Of course, removing things from this dataset risks the unforeseen breaking of reports build on it, and should be handled with care. With the “View Related” button you can see exactly which dashboards and reports depend on the selected dataset. Unfortunately, it does not show in which workspaces these reside, but we hope Microsoft will make this information available in a future update. Still, the greatest advantages of sharing datasets this way are:
- changes to the one dataset ensures updates for all other reports and
- security is easilyconfigured on workspace and dataset level.
These two advantages make tasks related to data management easier to execute.
Row Level Security (RLS) in shared datasets
Sharing datasets give users the ability to create new reports on validated and endorsed data models. Saving time and minimizing errors when building new reports. Additionally, with Row Level Security (RLS) enabled within the dataset, the same dataset can be used for different departments, groups or individuals. Financial data, for example, can be made visible for the finance department only, making sure other departments only see what they need to see in the same dataset.
The combination of RLS and dataset-sharing across workspaces makes data governance and security a lot easier as it is done on one location. Reusing the same dataset in multiple reports gives you one source of truth, one place to maintain security and one spot to test and validate the data.
Classic vs. Modern Workspaces
We often receive the question why some datasets can only be published to one workspace (the one in which it was created), while others can be published to multiple workspaces. There are two types of workspaces in Power BI: the classic workspace and the modern workspace. Only between modern workspaces it is possible to share datasets.
Classic workspaces
Classic workspaces are in fact Office 365 Groups. Groups in Office 365 are collections of collaborating people that share a set of resources, like a shared Outlook inbox and a shared calendar. In case you create a SharePoint site or a team in Teams, you create (amongst other things) an Office 365 group. This group is visible in Power BI as a classic workspace, but it is not the same kind of workspace as the modern workspace created in Power BI itself.
Modern workspaces
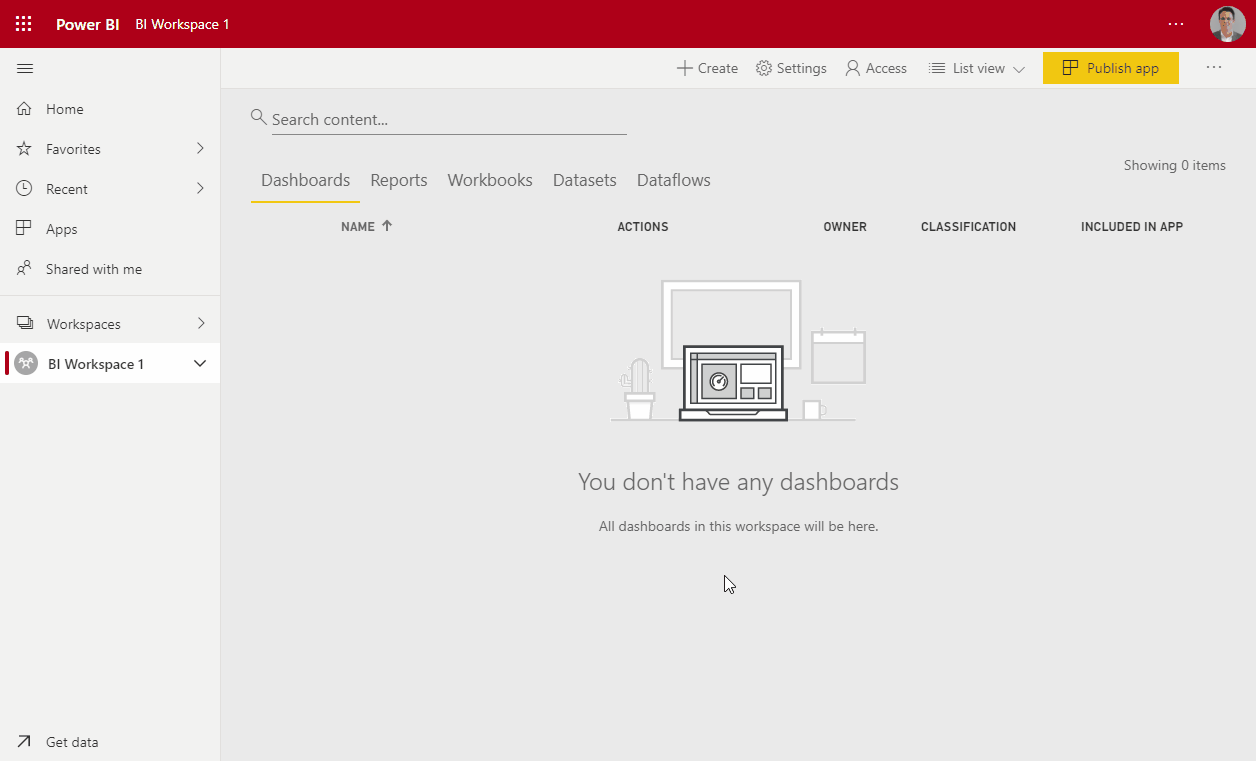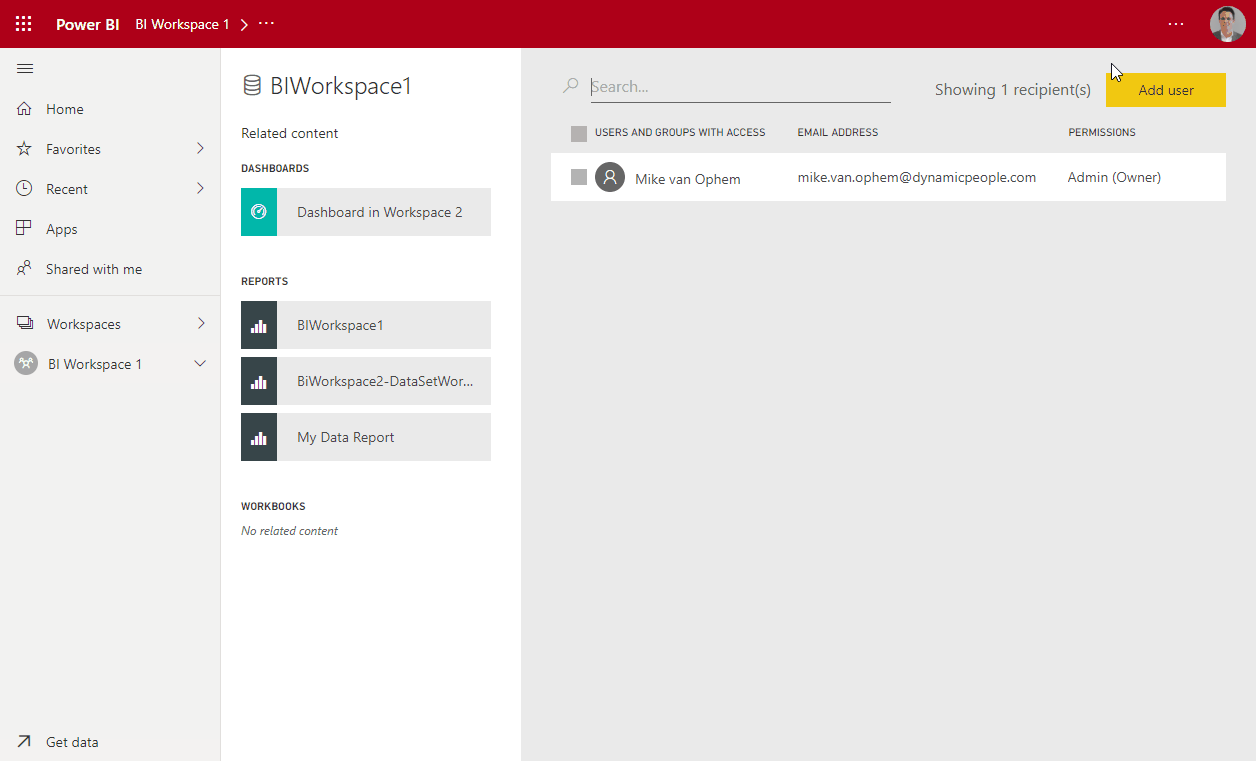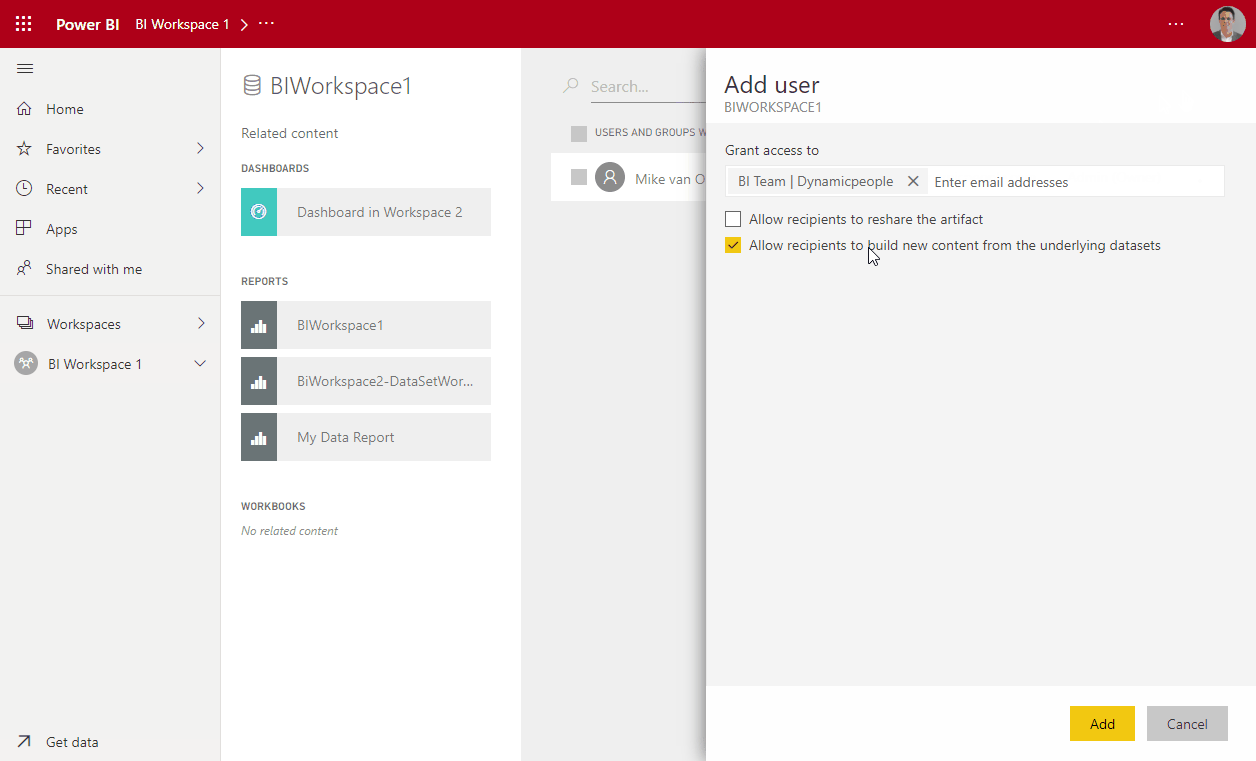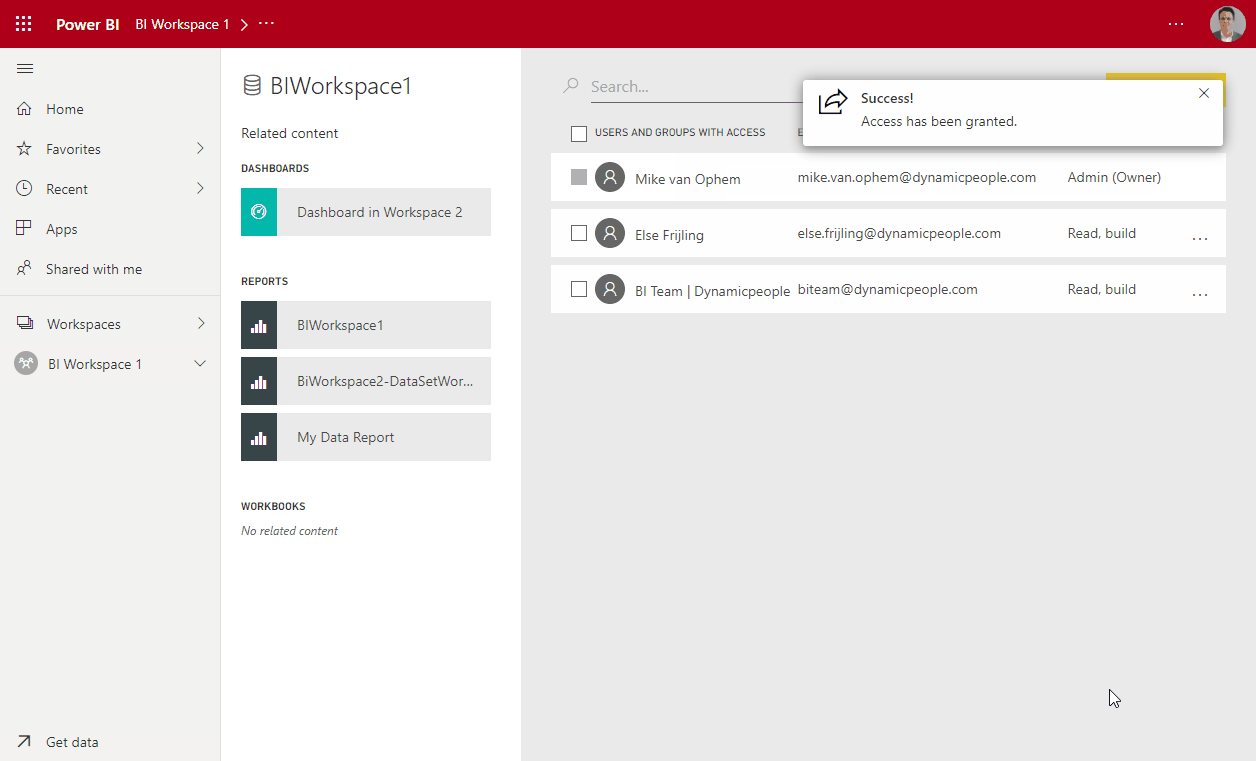
Modern workspaces are created in the Power BI online service (or power shell). In contrast to classic workspaces, modern workspaces are only used within Power BI. These workspaces are not based on the creation of an Office 365 Group. However, you can give an Office 365 Group access to a modern workspace and its content. There are four different access types: admin, member, contributor and viewer. With viewer-access you do not have editing rights. It is important to note that admin-, member- or contributor-access have editing rights and overwrites the roles defined by RLS. These security options allow you setting up security once, after which you only have to publish your dataset once.
BI as Self Service
We strongly believe that businesses should be able to generate actionable insights from their data and to service themselves in the field of business intelligence. Especially the second part, to service themselves, is now not only easier, but also more structured and secure.
Creating datasets should be done by the business itself.By the people who know what the most important questions are,who know the business and who know the data. These individuals should be well trained in data modelling with the Power BI desktop, so they are able to create the datasets needed by the business. Additionally, they should be well trained in governance and security in the Power BI service, making sure data governance and security is well maintained.
How to secure datasets and workspaces
- Create a modern workspace for the dataset, for example “Dataset-Workspace”.
- Give people who are responsible for the data model and its governance admin-, contributor-or member-access.
- Create a modern workspace for each department or user group that need access to the dataset, such as “Finance”.
- Give the Finance group viewer-access to the “Dataset-Workspace” or no rights at all.
- Share the dataset from the “Dataset-Workspace” with the Financegroup or select separate individuals.
- Assign them read and build rights. Sharing rights are optional.
- In case you enabled Row Level Security (RLS),assign a role to every individual or group that will use the dataset.
- If someone tries to use the dataset or read a report based on this dataset without having a role assigned they will get an error.
The dataset determines what a user can see if RLS is defined. Even though, the report developers can limit what users can see by adding filters, they will never see more than what is defined with RLS. The other way around is valid as well. Consider the following situation:
Tony and Nicola both work for Contoso Systems. Tony works for the USA area and Nicola is responsible for USA and EU, she is part of the MT. Tony can only see the data of Contoso System USA. Nicola can see the data of USA and EU.Tony creates a report to show the turnover per product group in the USA. The report shows him only the data for Contoso Systems USA, because Tony has a RLS role assigned for USA data only. However, when Nicola opens the same report she will see the data of Contoso Systems USA and EU combined. It could be that this might not have been the intention of Tony as he was not aware of the different RLS roles. Therefore, it is important to document the contents of the report, the dataset, and if applicable: the roles defined by RLS.

Conclusion
The new functionality of sharing datasets across workspaces works great with modern workspaces. Sharing datasets saves time, ensures one version of the truth and makes security and governance easy. However, be carefull when giving access to a workspaces where datasets are maintained. Giving rights to a workspace as admin, contributor or member overrules the Row Level Security assigned to users.
Need help or training to setup the environment for Power BI? Just give us a call.