Crud operations in Azure Cosmos Database
In this blog, we will learn how to create Azure Cosmos Database CRUD (Create, Update, Read, Delete) Operations in the employee management web application (C#).
Before starting the application, we must know: why the Azure Cosmos database?
NoSQL – Azure Cosmos DB supports NoSQL database, which makes it an easy and modern way for development.
Structure less – We can save the various type of data in a database container.
Speed – With very low latency and high availability, Microsoft gave a good SLA (Service Level Agreement) for the Cosmos DB.
Throughput – Very high throughput on all scales, and the guarantee of availability is 99.999%.
Fully managed – Similar to other services of Azure, we do not need to do the maintenance like applying patches or updates, so there is less administrative work.
Use – Nowadays, we can use this service in almost all types of applications like web, mobile, gaming, IoT and Telematics, Retail, and marketing.
Below are the steps to create a C# web application.
1. Create a sample web application named AppCosmosDBCurdOperations
2. Add a new folder name as Models and a class Employee. cs as the below code:
3. Add a new folder named Services, and Add an Interface named ICosmosDbServices.cs. Below is a sample code.
{
Task<IEnumerable<Employee>> GetItemsAsync(string query);
Task<Employee> GetItemAsync(string id);
Task AddItemAsync(Employee item);
Task UpdateItemAsync(string id, Employee item);
Task DeleteItemAsync(string id);
}
4. Create the new class CosmosDbService.cs and Implement the interface.
public class CosmosDbService : ICosmosDbService
{
private Container _container;
public CosmosDbService(
CosmosClient dbClient,
string databaseName,
string containerName)
{
this._container = dbClient.GetContainer(databaseName, containerName);
}
public async Task AddItemAsync(Employee item)
{
await this._container.CreateItemAsync<Employee>(item, new PartitionKey(item.Id));
}
public async Task DeleteItemAsync(string id)
{
await this._container.DeleteItemAsync<Employee>(id, new PartitionKey(id));
}
public async Task<Employee> GetItemAsync(string id)
{
try
{
ItemResponse<Employee> response = await this._container.ReadItemAsync<Employee>(id, new PartitionKey(id));
return response.Resource;
}
catch (CosmosException ex) when (ex.StatusCode == System.Net.HttpStatusCode.NotFound)
{
return null;
}
}
public async Task<IEnumerable<Employee>> GetItemsAsync(string queryString)
{
var query = this._container.GetItemQueryIterator<Employee>(new QueryDefinition(queryString));
List<Employee> results = new List<Employee>();
while (query.HasMoreResults)
{
var response = await query.ReadNextAsync();
results.AddRange(response.ToList());
}
return results;
}
public async Task UpdateItemAsync(string id, Employee item)
{
await this._container.UpsertItemAsync<Employee>(item, new PartitionKey(id));
}
}
5. Install the required NuGet packagesAzure.Cosmos and Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.
6. Update the Startup.cs file using the below code.
public Startup(IConfiguration configuration)
{
Configuration = configuration;
}
public IConfiguration Configuration { get; }
// This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to add services to the container.
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddRazorPages();
services.AddSingleton<ICosmosDbService>(InitializeCosmosClientInstanceAsync(Configuration.GetSection(“CosmosDb”)).GetAwaiter().GetResult());
}
// This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to configure the HTTP request pipeline.
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env)
{
if (env.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
}
else
{
app.UseExceptionHandler(“/Error”);
// The default HSTS value is 30 days. You may want to change this for production scenarios, see https://aka.ms/aspnetcore-hsts.
app.UseHsts();
}
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseRouting();
app.UseAuthorization();
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints =>
{
endpoints.MapRazorPages();
});
}
/// <summary>
/// Creates a Cosmos DB database and a container with the specified partition key.
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
private static async Task<CosmosDbService> InitializeCosmosClientInstanceAsync(IConfigurationSection configurationSection)
{
string databaseName = configurationSection.GetSection(“DatabaseName”).Value;
string containerName = configurationSection.GetSection(“ContainerName”).Value;
string account = configurationSection.GetSection(“Account”).Value;
string key = configurationSection.GetSection(“Key”).Value;
Microsoft.Azure.Cosmos.CosmosClient client = new Microsoft.Azure.Cosmos.CosmosClient(account, key);
CosmosDbService cosmosDbService = new CosmosDbService(client, databaseName, containerName);
Microsoft.Azure.Cosmos.DatabaseResponse database = await client.CreateDatabaseIfNotExistsAsync(databaseName);
await database.Database.CreateContainerIfNotExistsAsync(containerName, “/id”);
return cosmosDbService;
}7. Add the required configurations in AppSettings.json files as below.
“CosmosDb”: {
“Account”: “https://XXXXXXXXXXXX.documents.azure.com:443/”,
“Key”: “xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx”,
“DatabaseName”: “employeemanagement”,
“ContainerName”: “empcontainer”
}8. As per the SOLID principle it is good to keep separate the service part and front-end part, but this is the demo application so we will create the front-end part in the same application. So, let’s create the folder inside the page folder with the name Employee and add three Razor pages as below:
ListEmployee.cshtml, RegisterEmployee.cshtml, UpdateEmployee.cshtml
- ListEmployee.cshtml:
@page
@model AppCosmosDBCurdOperations.Pages.Employees.ListEmployeeModel
@{
ViewData[“Title”] = “ListEmployee”;
}
<h4>All Employees</h4>
<table class=”table”>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Employee[0].Name)
</th>
<th>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Employee[0].Email)
</th>
<th>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Employee[0].DoB)
</th>
<th>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Employee[0].Status)
</th>
<th></th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
@if (Model.Employee == null) { return; }
@foreach (var item in Model.Employee)
{
<tr>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Name)
</td>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Email)
</td>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.DoB)
</td>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Status)
</td>
<td>
<form method=”post”>
<button asp-page-handler=”EditEmployee” asp-route-id=”@item.Id” class=”btn btn-default bi bi-pencil”></button> |
<button class=”btn btn-default bi bi-trash” asp-page-handler=”DeleteEmployee” asp-route-id=”@item.Id”></button>
</form>
</td>
</tr>
}
</tbody>
</table>- ListEmployee.cshtml.cs:
using AppCosmosDBCurdOperations.Models;
using AppCosmosDBCurdOperations.Services;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.RazorPages;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace AppCosmosDBCurdOperations.Pages.Employees
{
public class ListEmployeeModel : PageModel
{
private readonly ICosmosDbService _cosmosDbService;
public ListEmployeeModel(ICosmosDbService cosmosDbService)
{
_cosmosDbService = cosmosDbService;
}
public IList<Employee> Employee { get; set; }
public async Task OnGetAsync()
{
await GetAllEmployees();
}
private async Task GetAllEmployees()
{
var lstEmployee = await _cosmosDbService.GetItemsAsync(“select * from c”);
Employee = lstEmployee.ToList();
}
public async Task OnPostDeleteEmployee(string id)
{
await _cosmosDbService.DeleteItemAsync(id);
await GetAllEmployees();
}
public IActionResult OnPostEditEmployee(string id)
{
return Redirect(“/Employees/UpdateEmployee?id=” + id);
}
}
}- RegisterEmployee.cshtml:
@page
@model AppCosmosDBCurdOperations.Pages.Employees.RegisterEmployeeModel
@{
ViewData[“Title”] = “RegisterEmployee”;
}
<h4>Register Employee</h4>
<hr />
<div class=”row”>
<div class=”col-md-4″>
<form method=”post”>
<div asp-validation-summary=”ModelOnly” class=”text-danger”></div>
<div class=”form-group”>
<label asp-for=”Employee.Name” class=”control-label”></label>
<input asp-for=”Employee.Name” class=”form-control” />
<span asp-validation-for=”Employee.Name” class=”text-danger”></span>
</div>
<div class=”form-group”>
<label asp-for=”Employee.Email” class=”control-label”></label>
<input asp-for=”Employee.Email” class=”form-control” />
<span asp-validation-for=”Employee.Email” class=”text-danger”></span>
</div>
<div class=”form-group”>
<label asp-for=”Employee.DoB” class=”control-label”></label>
<input asp-for=”Employee.DoB” class=”form-control” />
<span asp-validation-for=”Employee.DoB” class=”text-danger”></span>
</div>
<div class=”form-group”>
<label asp-for=”Employee.Status” class=”control-label”></label>
<select asp-for=”Employee.Status” class=”form-control”>
@foreach (var _status in Enum.GetValues(typeof(Models.EmployeeStatus)))
{
<option value=”@_status”>@_status</option>
}
</select>
<span asp-validation-for=”Employee.Status” class=”text-danger”></span>
</div>
<div class=”form-group”>
<input type=”submit” value=”Create” class=”btn btn-primary” />
</div>
</form>
</div>
</div>
@section Scripts {
@{await Html.RenderPartialAsync(“_ValidationScriptsPartial”);}
}- RegisterEmployee.cshtml.cs:
using AppCosmosDBCurdOperations.Models;
using AppCosmosDBCurdOperations.Services;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.RazorPages;
using System;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace AppCosmosDBCurdOperations.Pages.Employees
{
public class RegisterEmployeeModel : PageModel
{
private readonly ICosmosDbService _cosmosDbService;
public RegisterEmployeeModel(ICosmosDbService cosmosDbService)
{
_cosmosDbService = cosmosDbService;
}
public IActionResult OnGet()
{
return Page();
}
[BindProperty]
public Employee Employee { get; set; }
// To protect from overposting attacks, see https://aka.ms/RazorPagesCRUD
public async Task<IActionResult> OnPostAsync()
{
if (!ModelState.IsValid)
{
return Page();
}
Employee.Id = Guid.NewGuid().ToString();
await _cosmosDbService.AddItemAsync(Employee);
return RedirectToPage(“/Employees/ListEmployee”);
}
}
}- UpdateEmployee.cshtml:
@page
@model AppCosmosDBCurdOperations.Pages.Employees.UpdateEmployeeModel
@{
ViewData[“Title”] = “UpdateEmployee”;
}
<h4>Update Employee</h4>
<hr />
<div class=”row”>
<div class=”col-md-4″>
<form method=”post”>
<div asp-validation-summary=”ModelOnly” class=”text-danger”></div>
<input type=”hidden” asp-for=”Employee.Id” />
<div class=”form-group”>
<label asp-for=”Employee.Name” class=”control-label”></label>
<input asp-for=”Employee.Name” class=”form-control” />
<span asp-validation-for=”Employee.Name” class=”text-danger”></span>
</div>
<div class=”form-group”>
<label asp-for=”Employee.Email” class=”control-label”></label>
<input asp-for=”Employee.Email” class=”form-control” />
<span asp-validation-for=”Employee.Email” class=”text-danger”></span>
</div>
<div class=”form-group”>
<label asp-for=”Employee.DoB” class=”control-label”></label>
<input asp-for=”Employee.DoB” class=”form-control” />
<span asp-validation-for=”Employee.DoB” class=”text-danger”></span>
</div>
<div class=”form-group”>
<label asp-for=”Employee.Status” class=”control-label”></label>
<select asp-for=”Employee.Status” class=”form-control”>
@foreach (var _status in Enum.GetValues(typeof(Models.EmployeeStatus)))
{
<option value=”@_status”>@_status</option>
}
</select>
<span asp-validation-for=”Employee.Status” class=”text-danger”></span>
</div>
<div class=”form-group”>
<input type=”submit” value=”Save” class=”btn btn-primary” />
</div>
</form>
</div>
</div>
@section Scripts {
@{await Html.RenderPartialAsync(“_ValidationScriptsPartial”);}
}- UpdateEmployee.cshtml.cs:
using AppCosmosDBCurdOperations.Models;
using AppCosmosDBCurdOperations.Services;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.RazorPages;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace AppCosmosDBCurdOperations.Pages.Employees
{
public class UpdateEmployeeModel : PageModel
{
private readonly ICosmosDbService _cosmosDbService;
public UpdateEmployeeModel( ICosmosDbService cosmosDbService)
{
_cosmosDbService = cosmosDbService;
}
[BindProperty]
public Employee Employee { get; set; }
public async Task<IActionResult> OnGetAsync(string id)
{
if (id == null)
{
return NotFound();
}
Employee = await _cosmosDbService.GetItemAsync(id);
if (Employee == null)
{
return NotFound();
}
return Page();
}
// To protect from overposting attacks, enable the specific properties you want to bind to.
// For more details, see https://aka.ms/RazorPagesCRUD.
public async Task<IActionResult> OnPostAsync()
{
if (!ModelState.IsValid)
{
return Page();
}
try
{
await _cosmosDbService.UpdateItemAsync(Employee.Id, Employee);
}
catch (DbUpdateConcurrencyException)
{
if (!EmployeeExists(Employee.Id))
{
return NotFound();
}
else
{
throw;
}
}
return RedirectToPage(“/Employees/ListEmployee”);
}
private bool EmployeeExists(string id)
{
var emp = _cosmosDbService.GetItemAsync(id);
return emp != null;
}
}
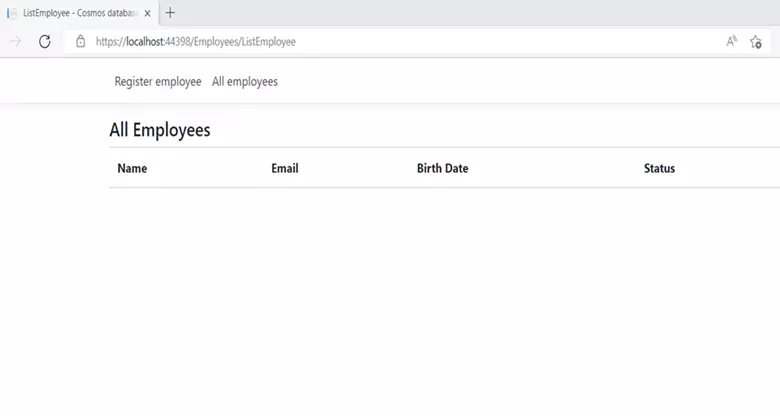
}9. And now it’s time to execute the application. Below are the screenshots after the application run.
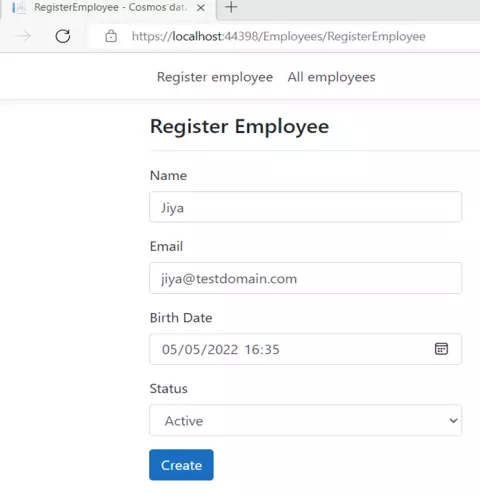
Register the employee:
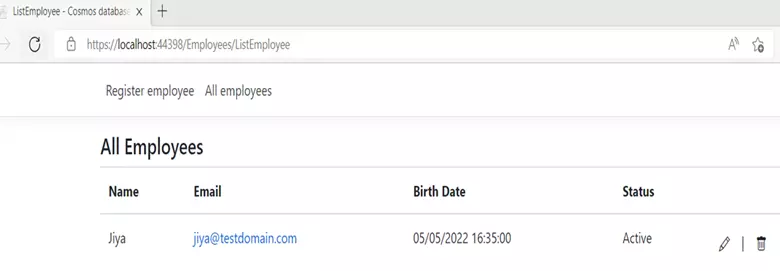
After creating the employee:
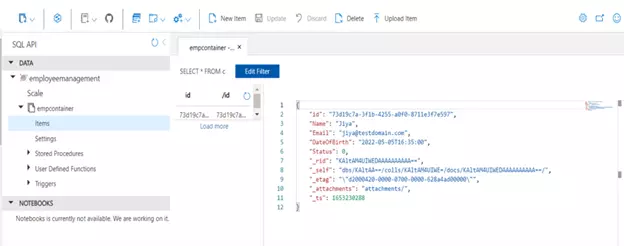
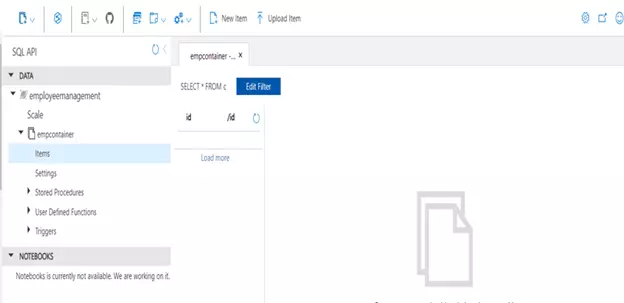
Below is from the Cosmos database:
Now, update the data.
From Cosmos DB:
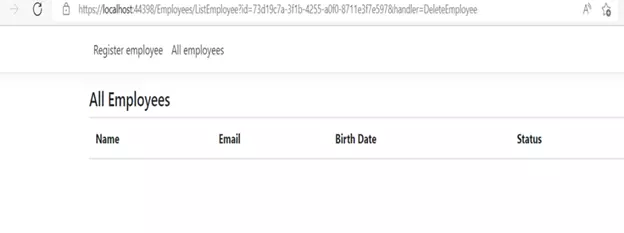
After the delete button is clicked:
Record deleted from the Cosmos database:
This concludes the blog about Azure Cosmos DB. See you in the next blog!